模式定义
为其他对象提供一种代理,以控制对这个对象的访问。代理对象起到中介作用,可以去掉功能服务或者增加额外的功能服务。
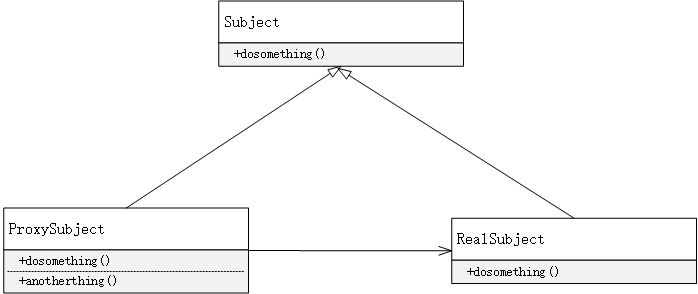
静态代理
代理和被代理对象在代理之前是确定的。他们都是事先相同的接口或者继承相同的抽象类。
创建一个接口Moveable,Car继承Moveable接口,要求用代理类来记录Car的运行时间。
Car继承Moveable接口:
|
|
Car:
|
|
继承实现静态代理
|
|
聚合实现静态代理
|
|
- 考虑到继承方式扩展代理功能的不方便,推荐使用聚合实现静态代理。也就是代理类和实际类实现共同的接口,代理类中包含所实现接口的引用。
|
|
|
|
|
|
动态代理
前面实现了Car类的静态代理,为其添加了运行时间记录和日志记录的功能。如果需要为火车或者自行车添加类似的功能,需要重新定义相同的类,类十分臃肿,同时代码重用性不高,因此引入了动态代理,也就是在程序
jdk动态代理
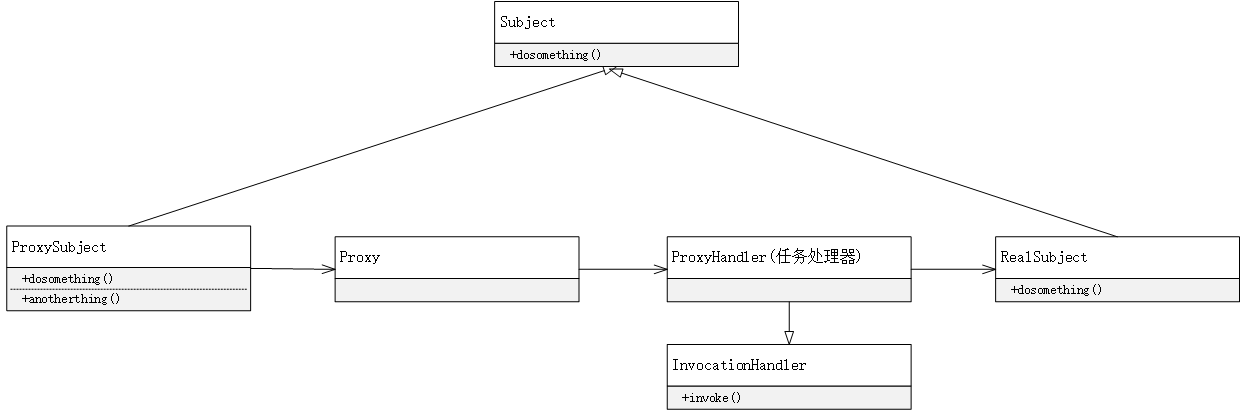
- InvocationHandler接口,接口中定义了一个invoke方法,invoke方法中第一个参数表示代理类,第二个参数指被代理的方法,args指该方法的参数数组。这个抽象方法会在代理类中动态实现。
|
|
- Proxy:该类为动态代理类,其中的newProxyInstance方法返回一个代理类实例,返回后的代理类可以被当做代理类使用,可使用被代理类的在接口中声明过的方法。
|
|
动态代理实现步骤
- 创建一个实现接口InvocationHandler的类,实现invoke方法
|
|
- 创建被代理的类以及接口(Car以及Moveable)
- 调用Proxy的静态方法,创建一个代理类
- 通过代理调用方法
|
|
JDK动态代理与CGLIB动态代理的区别
| jdk动态代理 | CGLIB动态代理 |
|---|---|
| 只能代理实现了接口的类 | 针对类来实现代理 |
| 没有实现接口的类不能实现JDK动态代理 | 对指定目标类产生一个子类,通过方法拦截技术拦截所有父类方法调用 |
| JDK动态代理利用反射机制生成一个实现代理接口的匿名类,在调用具体方法前调用InvocationHandler来处理 | cglib是利用asm开源包,对代理对象的class文件加载进来,通过修改其字节码生成子类来处理 |
模拟JDK动态代理的实现
实现功能,通过Proxy的newproxyInstance返回代理对象
1、声明一段源码,动态产生代理
2、编译源码,产生新的类
3、将这个类load到内存中,产生一个新的对象
4、return代理对象
handler:
|
|
proxy:
|
|


