Redis介绍
redis是一个基于键值对的分布式存储系统,与memcached类似,却优于memcached的一个高性能的key-value数据库。其中键值对的key总是为一个字符串对象,字符串的值可以为字符串对象,列表对象,哈希对象,集合对象,有序集合对象之一。
Redis中value的值为上面五种,但是底层数据结构包括:
- 简单动态字符串
- 链表
- 字典
- 跳跃表
- 整数集合
- 压缩列表
- 对象
简单动态字符串(simple dynamic string)
介绍
Redis底层是由C编写的,但是其对C中字符串做了一个封装,构建了种名为简单动态字符串的抽象类型,并将SDS设置为redis默认采用的字符串表示
|
|
key是一个字符串对象,字符串对象的低层是一个保存着“msg”的SDS;
value是一个字符串对象,低层是一个保存着字符串“sdsTest”的SDS。
SDS的定义
redis中定义动态字符串的结构:
|
|
则msg可以被表示为:

- len为7,表示这个sds的长度为7
- free为0,表示这个sds可用空间为0
- buf是一个char数组,分配了len + 1 + free个字节的长度,前len个字节保存着SDS的信息,接下来一个字符保存字符串终止符’\0’,剩下free个字节是未使用的。
SDS与C字符串的区别
redis不直接使用C字符串而采用SDS的原因主要在于传统C语言使用长度为N+1的字符数组来存储长度为N的字符串,这样在获取字符串长度,字符串扩展操作时效率低,不能满足redis对字符串在安全性、功能、效率等的要求。
获取字符串长度
- 传统C语言:获取字符串长度需要遍历字符数组,复杂度为O(N);
- Redis SDS:获取len属性的值就是字符串的长度 O(1);
杜绝缓冲区溢出
- C语言中字符串不记录字符串的长度,容易造成缓冲区溢出。比如拼接字符串过程容易发生缓冲区溢出。
- redis中sds的空间分配策略杜绝了发生缓冲区溢出:redis会在拼接字符串之前,预先检查给定SDS空间是否足够,如果不够会先扩展SDS空间,然后再执行拼接操作。
减少修改字符串时带来的内存重新分配次数。
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950/* Enlarge the free space at the end of the sds string so that the caller* is sure that after calling this function can overwrite up to addlen* bytes after the end of the string, plus one more byte for nul term.** Note: this does not change the *length* of the sds string as returned* by sdslen(), but only the free buffer space we have. */sds sdsMakeRoomFor(sds s, size_t addlen) {void *sh, *newsh;size_t avail = sdsavail(s);size_t len, newlen;char type, oldtype = s[-1] & SDS_TYPE_MASK;int hdrlen;/* Return ASAP if there is enough space left. */if (avail >= addlen) return s;len = sdslen(s);sh = (char*)s-sdsHdrSize(oldtype);newlen = (len+addlen);if (newlen < SDS_MAX_PREALLOC)newlen *= 2;elsenewlen += SDS_MAX_PREALLOC;type = sdsReqType(newlen);/* Don't use type 5: the user is appending to the string and type 5 is* not able to remember empty space, so sdsMakeRoomFor() must be called* at every appending operation. */if (type == SDS_TYPE_5) type = SDS_TYPE_8;hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);if (oldtype==type) {newsh = s_realloc(sh, hdrlen+newlen+1);if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;} else {/* Since the header size changes, need to move the string forward,* and can't use realloc */newsh = s_malloc(hdrlen+newlen+1);if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;memcpy((char*)newsh+hdrlen, s, len+1);s_free(sh);s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;s[-1] = type;sdssetlen(s, len);}sdssetalloc(s, newlen);return s;}C语言在进行字符串的扩展和收缩的时候,都会面临着内存空间的重新分配问题。字符串拼接会产生字符串的内存空间的扩充,忘记申请分配空间会导致内存溢出;而字符串切割的时候,如果没有对内存空间重新分配会造成内存泄漏。
redis对SDS进行扩展,修改是SDS的长度,通过预分配侧率,SDS将连续增长的N次字符串所需的内存重分配次数从固定N次,降低为最多N次。
惰性空间的释放
redis字符串进行收缩时,修改free属性来记录剩余的空间,并不直接回收那些不使用的内存,这样可以避免下次对字符串再次修改过程中可能存在的空间扩展,避免了缩短字符串所需要的内存重分配操作和将来可能存在的增长字符串操作。
二进制安全
C语言中字符串以空字符串为结束符,所以传统字符串不能保存图片视频等二级制文件。redis中依靠len来判断字符串是否结束,而不是寻找空字符串,这样可以用来保存图片,音频,视频等二进制数据,实现了二级制安全。SDS遵循C字符串以空字符串结尾的惯例。
链表
链表在redis中使用很多,比如列表件的低层实现之一就是链表。而且在redis中链表的结构被实现为双向链表,收尾操作很快。
链表的数据结构
|
|
- 双向链表通过prev和next指针来会获取当前节点的前驱节点和后继节点的复杂度为O(1);
我们可以直接通过list来操作链表结构:
|
|
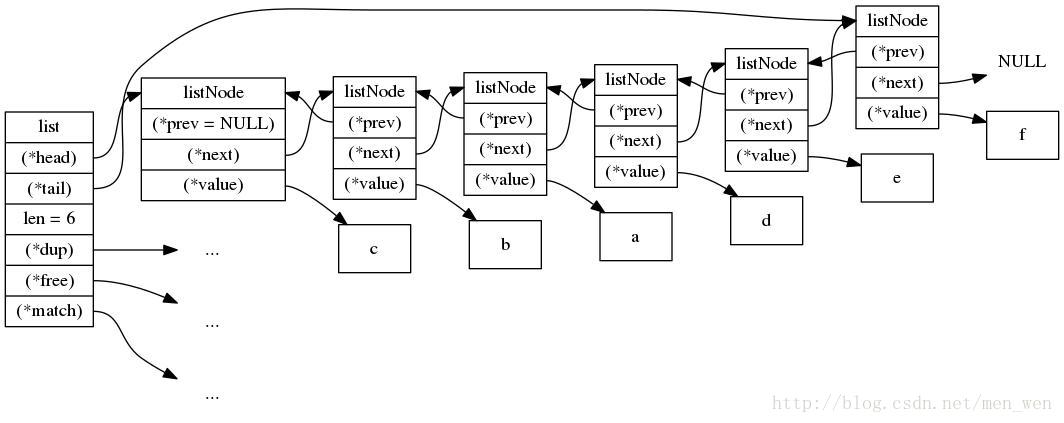
- 其中head指针指向链表头,tail指针指向链表尾,获取收尾节点复杂度O(1)
- len记载链表的长度 获取长度复杂度为O(1);
- dup,free,match指针实现多态,链表节点listNode使用空指针来保存节点的值,表头list使用dup,free, match指针来针对链表中存放非不同对象来实现不同的方法。
字典
或者成为map,是一种用于保存键值对的抽象数据结构。字典中一个key可以和一个value进行关联,每一个key独一无二并且指向一个value,一个value可以被多个可以同时指定。C语言中不存在字典这种数据结构,redis实现了字典的数据结构。redis存取数据采用的都是key-value的形式,其中key为一个字符串对象,而value取值可以是字符串,可以是列表,可以是集合等。
字典的实现
redis中字典是通过哈希表实现的,一个哈希表有多个节点,每个节点保存一个键值对。
|
|
- type: 指针指向dictType结构,该结构使得key和value能够存储任何类型的数据。
- privdata: 私有数据,存放dictType结构中的函数的参数
|
|
- ht[2]: 两张哈希表
|
|
|
|
- rehashidx: rehash的标志位
- iterators:记录迭代器的数量
Redis中使用的哈希算法
- 计算int的哈希函数
|
|
- MurmurHash2哈希算法:redis使用MurmurHash2算法来计算法哈希值,能产生32-bit或64-bit哈希值。该算法对硬件的要求在于:1.机器可以从任意一个地址读取一个4-bit大小的值,并且int的大小为4bit。seed默认值为5381,可以人为改变,不过没什么意义。
|
|
- djb哈希算法: seed和字符串的ascii值,len次变换之后得到hash值。
|
|
rehash
当哈希表的大小不能满足需求,可能会有两个以上的键值被分配到同一个位置上,这时候就发生了冲突,redis中解决冲突的方法和HashMap中类似,使用链表法。但是当这种情况频繁发生,会影响查找的性能,需要尽力避免。这个时候希望通过哈希表的load factor来动态的决定扩展哈希表或者收缩哈希表。
- rehash流程:
- 根据要求扩展或者收缩ht[1]
- 将ht[0]上的节点rehash到ht[1]上
- 释放ht[0], 将ht[1]设置为ht[0],新建一个ht[1]
扩展操作:
|
|
收缩操作:
|
|
根据传入的size来跳帧过着创建字典d的哈希表
|
|
rehash过程不是一次性集中完成的,而是分多次,渐进式的,断续进行的,这样可以减少对服务器的影响。
渐进式rehash(incremental rehashing)
- dict中有一个成员为rehashidx,表示rehash的状态标志,-1表示不进行rehash,0表示开始进行rehash。
- rehash过程中,每次对字典的CRUD时,会检查rehashidx标志位,如果在进行rehash,CRUD结束之后顺带进行单步rehash,同时rehashidx+1;
- rehash结束之后,将rehashidx该为-1。
|
|
跳跃表
跳跃表示一种有序的数据结构,它通过在每个节点中维持多个指向其他节点的指针,从而可以快速到达要访问的节点。跳跃表是一个有序链表,其查找复杂度平均为O(logN),最坏O(N)。redis中将跳跃表应用在有序集合键。
Redis中跳跃表主要有两部分组成:zskiplist和中skiplistNode:
|
|
- level:层,每个元素包含一个指向其他节点的指针,实现跳跃查询的关键。
整数集合
整数结合是集合键低层实现之一。集合键另一实现为值为空的散列表。整数集合是为了节省使用散列表存储整形对象时的空间浪费。
|
|
- encoding:编码格式,默认用2个字节存储,还有4个字节和8个字节
- length:集合元素的数量
- contents:数组类型
新的元素插入到集合的流程:
- 判断新元素的编码格式
|
|
- 调整内存空间
|
|
- 根据编码格式设置对应的值
|
|
数组集合的好处:提升灵活性并节省内存空间。
|
|
压缩列表
ziplist是哈希键的低层实现之一。为特殊编码的双向链表,和整数集合一样是为了提高内存的存储效率而的设计的。当保存的对象是小整数,或者长度较短的字符串,redis就会使用压缩列表来作为哈希键的实现。
压缩列表的构成
|
|
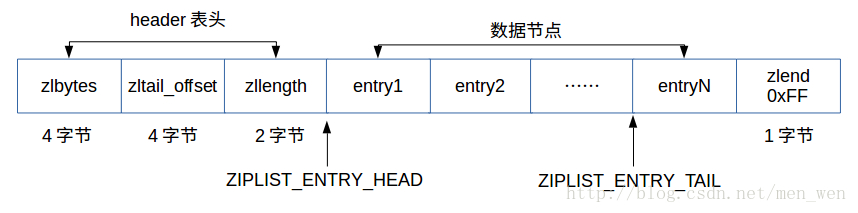
压缩链表可以包含任意多个节点,每个节点保存一个字节数组或者一个整数值。


